| 发布时间:2022-11-02 17:38:03 | 来源:本站原创 | 作者:本站编辑 | 浏览次数: |
原文标题: Strategies of disaster waste management after an earthquake: A sustainability assessment 原文作者(*通讯):Alessia Amato, Francesco Gabrielli, Francesco Spinozzi, Lorenzo Magi Galluzzi, Susanna Balducci, Francesca Beolchini* 作者单位:意大利马尔凯理工大学 关键词:灾害废弃物管理、地震、自然灾害、生命周期评估、经济分析 原文链接: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0921344919300965
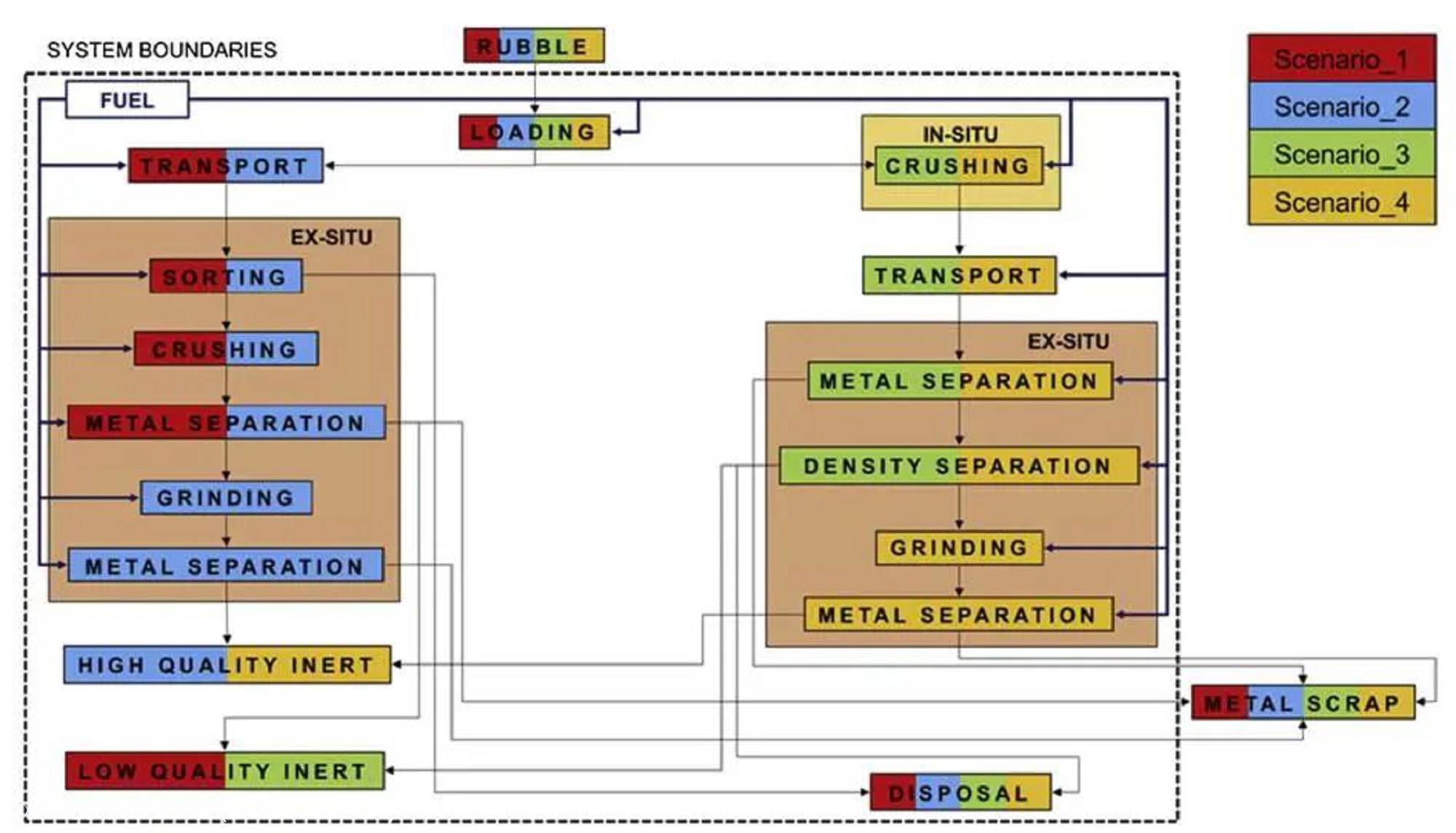
图片来源于网络(侵删) 文章亮点 (1)本研究回顾分析了灾害废弃物管理常见的方法 (2)估测了灾害废弃物管理对碳足迹和经济影响 2 文章导读 自然灾害每天都在地球上发生,对人口、自然和人类环境产生不同的影响。这些与每个地区的地理有关的事件包括:地质、水文或水文地质现象等(例如地震、洪水、滑坡、火山爆发、海啸和飓风)。在紧急情况发生后,快速有效的援助是必须认真考虑的,以保证对受灾民众的援助。事实上,这些重要的救援工作往往容易受到大量建筑废弃物障碍和碎石碎片的影响。因此,需要高效清除路障碎石等建筑废弃物,而清除碎石显然也有利于恢复受灾地区的正常状况,因为这一行动对改善受影响人口的身心健康至关重要。在灾害发生过程中,影响废弃物产生的主要因素是自然事件的强度和受灾地区的城市化程度。因此,废弃物管理可以视作有关工程的关键问题之一,而现阶段许多有关研究的就是朝着废弃物管理的良性未来迈进,以更好地保障环境和人类健康。 3 原文摘要 地震最重要的影响之一是产生大量的废弃物,而对碎石的不正确管理会造成相关的环境破坏、经济损失和对人们的心理影响。在此背景下,本文评估了废弃物管理的不同策略,并估计了碳足迹和经济影响从而确定最佳选择。总的来说,通过采用不同的管理方案,其成本和对环境的影响各不相同:可以使用临时储存场地、可以通过不同的技术(简单粉碎或高级精制)来处理碎石或者处理工作可以在距事故现场的不同距离进行。具体而言,环境影响评估证明了就地预处理碎石和强化精炼的重要性,其旨在获得高质量的惰性材料。另一方面,经济分析表明,最好的选择是把所有物品都运输到对应的处理地点,再对碎石进行简单的处理。因此,本研究的评估得出了相互矛盾的结论:从环境的角度来看,加强对碎石的处理是积极的,但对管理成本的增加是消极的。相关的经济标准现阶段在很大程度上推动应急管理人员作出相关决定;然而,环境负荷可能产生长期影响从而造成更显著的经济影响,这也是不可忽视的。 图1. LCA分析中考虑的系统边界 图2. 对四种设想方案所产生的环境影响的估测 图3. 对四种考虑的情景所产生的经济影响的估计 4 原文信息 5 Abstract One of the most significant effects of an earthquake is the production of a huge amount of waste. An incorrect management of the rubbles causes relevant environmental damages, economic losses and a psychological impact for the population. In this context, the present manuscript assesses different strategies of waste management, estimating the carbon footprint and the economic impact, in order to define the best choices. Overall, different management options can be applied, that have different costs and impacts on the environment: a temporary storage site could be used, rubbles can be treated through different technologies (either simple crushing or advanced refining), and the treatment can be carried out at different distances from the site of the event. The environmental impact assessment evidenced the importance of an in-situ pre-treatment of the rubbles and of an enhanced refining, addressed at the achievement of high quality inert. On the other hand, the economic analysis suggests that the best option is to transport everything to the treatment site, and to carry out a simple treatment of the rubbles. Consequently, our assessment resulted in conflicting conclusions, where an enhanced treatment of the rubbles is positive, from an environmental point of view, but negative, for the increase in the management costs. The economic criteria are currently pushing any decision taken by the emergency managers; however, the environmental load may have a long-term effect with even more significant economic consequences, and it cannot be neglected. 本期编辑



周桢佺,思特雅大学工程与建筑环境学院,博士研究生在读,研究方向:可持续建筑与项目管理。



